Provenance statements are a way to establish where a package was built and who published a package, which can increase supply-chain security and transparency for the packages.
You can read about this in more detail in the npm documentation.
Having a provenance statement doesn’t guarantee the package has no malicious code. Instead, npm provenance provides a verifiable link to the package’s source code and build instructions, which developers can then audit and determine whether to trust it or not.
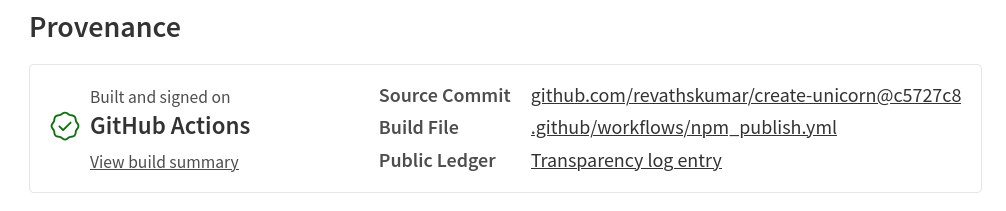
In order to publish the npm package with a provenance statement, the package must be built on a supported cloud CI/CD provider.
This blog post explains how to publish the package with a provenance statement using GitHub actions.
Generate npm granular access token
First, let’s generate a new npm granular access token with write permission. If your package already has a published version, you can generate a token for that specific package that you intend to publish.
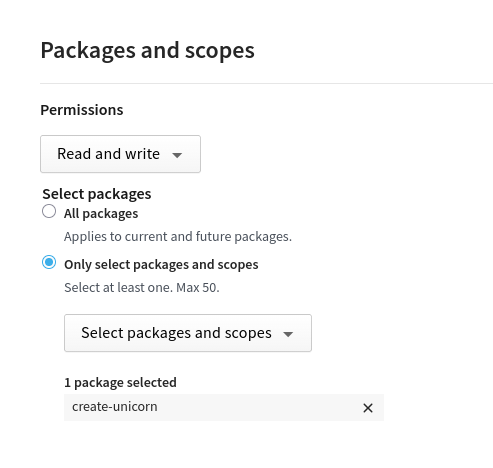
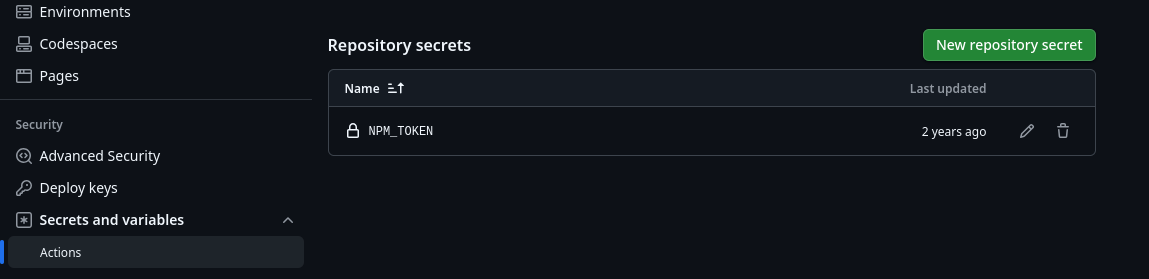
Once you have the new token, Goto
Github Repository > Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions
and add to repository secrets.
Github Action
Next, add the github action to publish the package on a new tag event.
# .github/workflows/npm_publish.yml
name: Publish Package to npmjs
on:
push:
tags: "*"
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
id-token: write
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: "24.x"
registry-url: "https://registry.npmjs.org"
- run: npm ci
- run: npm publish --provenance --access public
env:
NODE_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}Make sure that your command to publish include --provenance flag like
npm publish --provenance --access public
Hope that is helpful.
Thank you.